Abstract
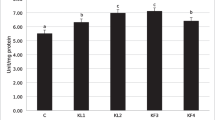
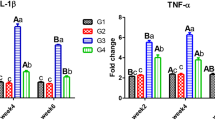
The aim of the present work was to study the alleviative properties of thiamine-supplemented fish diet on serum levels of Pb and some biochemical alterations provoked by Pb intoxication in carp. Fish in group 1 formed the untreated control group while fish in groups 2 and 3 received lead acetate (5 ppm) for 15 days. Group 3 was administered with thiamine (50 mg/kg diet) during lead exposure. The results revealed significantly raised levels of circulating Pb and malondialdehyde in group 2 compared to the control group. Significant decreases in circulating Pb and malondialdehyde contents in group 3 were observed following thiamine administration, as compared to group 2. Plasma values of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), urea, creatinine, and uric acid increased in group 2 compared to the control group, although the increase was only significant (p < 0.05) for ALT and creatinine. Thiamine supplementation effectively decreased ALT and creatinine concentrations to the levels observed in the apparently healthy controls. The other plasma biochemical indices quantified did not exhibit any significant modifications among experimental groups. These results are indicative of some variations caused by Pb intoxication in some plasma indices which signify the toxicity of Pb in Cyprinus carpio. Moreover, co-administration of thiamine with Pb notably reversed the expression of circulating biochemical biomarkers provoked by lead poisoning.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adegbesan BO, Adenuga GA (2007) Effect of lead exposure on liver lipid peroxidative and antioxidant defense systems of protein-undernourished rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 116:219–225
Al-Asgah NA, Abdel-Warith AW, Younis e-SM, Allam HY (2015) Haematological and biochemical parameters and tissue accumulations of cadmium in Oreochromis niloticus exposed to various concentrations of cadmium chloride. Saudi J Biol Sci 22(5):543–550
Aykin-Burns N, Laegeler A, Kellogg G, Ercal N (2003) Oxidative effects of lead in young and adult Fisher 344 rats. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 44:417–420
Benzie IF, Strain JJ (1996) The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: the FRAP assay. Anal Biochem 239:70–76
Beytut E, Yuce A, Kamiloglu NN, Aksakal M (2003) Role of dietary vitamin E in cadmium-induced oxidative damage in rabbit’s blood, liver and kidneys. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 73:351–355
Bokara KK, Brown E, McCormick R, Yallapragada PR, Rajanna S, Bettaiya R (2008) Lead-induced increase in antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxidation products in developing rat brain. Biometals 21:9–16
Coppock RW, Wagner W, Reynolds JD, Vogel RS, Gelberg HB, Florence LZ, Wolff WA (1991) Evaluation of edentate and thiamine for treatment of experimentally induced environmental lead poisoning in cattle. Am J Vet Res 52:1860–1865
Farombi EO, Adelowo OA, Ajimoko YR (2007) Biomarkers of oxidative stress and heavy metal levels as indicators of environmental pollution in African cat fish (Clarias gariepinus) from Nigeria Ogun river. Int J Environ Res Public Health 4(2):158–165
Firat O, Cogun HY, Yüzereroglu TA, Gok G, Firat O, Kargin F, Kotemen Y (2011) A comparative study on the effects of a pesticide (cypermethrin) and two metals (copper, lead) to serum biochemistry of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Physiol Biochem 37:657–666
Flora SJ, Tandon S (1986) Preventive and therapeutic effects of thiamine, ascorbic acid and their combination in lead intoxication. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 58:374–378
Flora SJ, Pande M, Mehta A (2003) Beneficial effect of combined administration of some naturally occurring antioxidants (vitamins) and thiol chelators in the treatment of chronic lead intoxication. Chem Biol Interact 145:267–280
Ghazaly KS (1991) Influences of thiamin on lead intoxication, lead deposition in tissues and lead hematological responses of Tilapia zillii. Comp Biochem Phsiol c 100:417–421
Kaila K, Swaran J, Flora S (2005) Strategies for safe and effective therapeutic measures for chronic arsenic and lead poisoning. J Occup Health 47:1–27
Karan V, Vitorovic S, Tutundzic V, Poleksic V (1998) Functional enzymes activity and gill histology of carp after copper sulfate exposure and recovery. Ecotoxol Environ Saf 40:49–55
Kim J, Kang J (2015) The lead accumulation and hematological findings in juvenile rock fish Sebastes schlegelii exposed to the dietary lead (II) concentrations. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 115:33–39
Ling Q, Hong F (2010) Antioxidative role of cerium against the toxicity of lead in the liver of Maiti AK, Saha NK, Paul G (2010) effect of lead on oxidative stress, Na+K+ATPase activity and mitochondrial electron transport chain activity of the brain of Clarias batrachus L. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 84(6):672–676
Maiti AK, Saha NC, Paul G (2010) Effect of lead on oxidative stress, Na+K+ATPase activity and mitochondrial electron transport chain activity of the brain of Clarias batrachus L. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 84(6):672–676
Masso Gonza lez EL, Antonio Garcia MT (2009) Natural antioxidants protect against lead-induced damage during pregnancy and lactation in rat's pups. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:2137–2142
Mirmazloomi S, Shahsavani D, Baghshani H (2015) Studies on the protective effects of ascorbic acid and thiamine on lead-induced lipid and protein oxidation as well as enzymatic alterations in some tissues of Cyprinus carpio. Comp Clin Pathol 24:1231–1236
Najarnezhad V, Aslani MR, Balalimood M (2010) The therapeutic potential of thiamine for treatment of experimentally induced subacute lead poisoning in sheep. Comp Clin Pathol 19:69–73
Ognjanovic BI, Pavlovic SZ, Maletic SD, Zikic RV, Stajn AS, Radojicic RM et al (2003) Protective influence of vitamin E on antioxidant defense system in the blood of rats treated with cadmium. Physiol Res 52:563–570
Pande M, Mehta A, Pant BP, Flora SJS (2001) Combined administration of a chelating agent and an antioxidant in the prevention and treatment of acute lead intoxication in rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 9:173–184
Patra RC, Swarup D, Dwivedi SK (2001) Antioxidant effects of a-tocopherol, ascorbic acid and L-methionine on lead induced oxidative stress to the liver, kidney and brain in rats. Toxicology 162:81–88
Patrick L (2006) Lead toxicity part II: the role of free radical damage and the use of antioxidants in the pathology and treatment of lead toxicity. Alternat Med Rev 11:114–127
Rajeshkumar S, Liu Y, Ma J, Duan HY, Li X (2017) Effects of exposure to multiple heavy metals on biochemical and histopathological alterations in common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. Fish Shellfish Immunol 70:461–472
Senapti SK, Dey S, Dwivedi SK, Patra RC, Swarup D (2000) Effect of thiamine hydrochloride on lead induced lipid peroxidation in rat liver and kidney. Vet Hum Toxicol 42:236–237
Shahsavani D, Baghshani H, Alishahi E (2011) Efficacy of allicin in decreasing lead (Pb) accumulation in selected tissues of lead-exposed common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Biol Trace Elem Res 142:572–580
Shahsavani D, Baghshani H, Aslani MR, Sadat-Fatemi F (2012) The impact of allicin on lead-induced oxidative damage in selected organs of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Comp Clin Pathol 21:769–775
Todorova I, Simeonova G, Kyuchukova D, Dinev D, Gadjeva V (2005) Reference values of oxidative stress parameters (MDA, SOD, CAT) in dogs and cats. Comp Clin Pathol 13:190–194
Vutukuru SS, Prabhath NA, Raghavender M, Yerramilli A (2007) Effect of arsenic and chromium on the serum amino-transferases activity in Indian major carp, Labeo rohita. Int J Environ Res Public Health 4:224–227
Wang C, Zhang Y, Liang J, Shan G, Wang Y, Shi Q (2006) Impacts of ascorbic acid and thiamine supplementation at different concentrations on lead toxicity in testis. Clin Chim Acta 370:82–88
Winston GW, Digiulio RT (1991) Prooxidant and antioxidant mechanisms in aquatic organisms. Aquat Toxicol 19:137–161
Funding
This work was supported by a grant (No. 21603) from Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Mashhad, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The experiment protocol was in compliance with the advices of Research Ethics Committee of Ferdowsi University of Mashhad.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nourian, K., Shahsavani, D. & Baghshani, H. Effects of lead (Pb) exposure on some blood biochemical indices in Cyprinus carpio: potential alleviative effects of thiamine. Comp Clin Pathol 28, 189–194 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2814-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2814-2